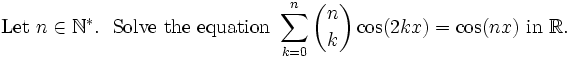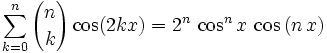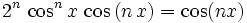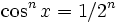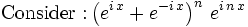Sol032106
Solution by landen
The left side of the problem can be summed(method below) in closed form to get:
Now we can solve:
We get a pile of solutions when nx is an odd multiple of π / 2, because cos(nx) = 0. When cos(nx) is non-zero, we can divide it out to get:
This provides an infinite set of solutions when cos(x) = 1 / 2. If n is even there is another set when cos(x) = − 1 / 2.
The trig identity justification
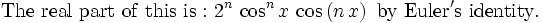
We can expand with the binary formula first, use Euler's identity, take the real part, and get exactly the sum we need so: